By Natalie Hanson
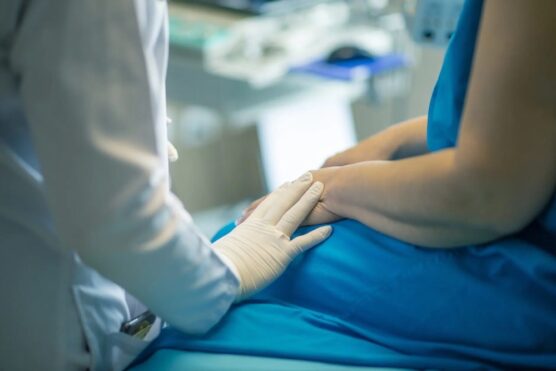
LOS ANGELES (CN) — The California Supreme Court breathed new life Monday into a lawsuit that accuses Aetna of having fired or threatened to fire physicians who referred patients to out-of-network providers.
Aetna had previously defeated the suit from the California Medical Association for lack of standing, but Associate Justice Kelli Evans wrote for the unanimous high court Monday that this was in error.
Appointed to the bench by Gov. Gavin Newsom, Evans said that the lower court had confused associational standing — in which a group can bring claims on behalf of members — with organizational standing, in which organization asserts claims based on its own injuries.
As alleged here, Evans wrote: “the perceived threat to CMA’s mission went beyond injury to physician members of CMA. By imposing unwarranted restrictions on network physicians’ medical referrals, in CMA’s view, Aetna’s policy impaired CMA’s efforts to protect the public health.”
A nonprofit professional association representing more than 37,000 California physicians, the California Medical Association applauded Monday’s decision.
“The practice of threatening physicians who refer patients to out-of-network providers is unlawful, and we are pleased that the court agrees that CMA has the right to challenge these practices in court,” Donaldo Hernandez, the group’s president, said in a statement.
While CMA claims that Aetna’s policy on provider referrals violated sections of the Insurance Code, Business and Professions Code and Health and Safety Code, Aetna argues that the policy was adopted in response to a practice of referrals being made to facilities in which the referring physician had financial interests. Aetna says the policy was designed to encourage participating physicians to use in-network care providers.
The merits of the case remain untested, however, because Aetna argued that the physician group lacked standing. Aetna said CMA had no direct business ties with the Aetna, nor could it clearly show how the policy caused it any injury.
CMA had brought the original lawsuit with multiple medical providers and associations, including the Los Angeles County Medical Association and the Santa Clara County Medical Association. By April 2019, however, all plaintiffs except the association agreed to dismiss their claims, and Aetna agreed to abandon its counterclaims to streamline litigation.
That November, the Los Angeles Superior Court granted Aetna’s motion for summary judgment on standing grounds. An appeals court later affirmed that finding, holding that the association could seek an injunction against Aetna only if it had individually suffered injury.
In reversing those decisions Monday, Evans said the association had in fact shown standing because it had shown it was losing money because of the in-network provider police.
The judge pointed to evidence showing that Aetna implemented its policy by communicating with physicians in preferred provider networks, in some cases threatening to terminate their network participation.
Evans called it “foreseeable,” not only that physicians would take this problem to CMA, “the state’s most prominent physician association,” but also that “CMA would come to their assistance by working to reverse or alter Aetna’s policy, attempting to prevent its implementation in ways that impinged on its members’ medical practices.” This meant the association had suffered financial injuries beyond just the costs of preparing for and fighting this specific lawsuit.
A spokesperson for Aetna declined to comment on the ruling.
In the ruling, Evans zeroed in on the issue of CMA’s standing — one of the most significant legal issues that has dogged the association through the case.
“This is not a case of an organization attempting to manufacture standing and insert itself into a dispute in which it had no natural stake,” Evans wrote for the court. “While voluntary in one sense — CMA, like many other organizations, is free to set its own budgetary priorities — its decision to expend resources on working to counter the perceived threat in Aetna’s policy followed from that policy in a sufficiently direct and uninterrupted causal chain.”
Chief Justice Patricia Guerrero and Justice Martin Jenkins, both Newsom appointees, concurred in the ruling, as did Brown appointees Goodwin Liu, Leondra Kruger, and Joshua Groban; and Carol Corrigan, a Schwarzenegger appointee.
Like this:
Like Loading...
Related




 Tweet This
Tweet This Facebook
Facebook Digg This
Digg This Bookmark
Bookmark Stumble
Stumble RSS
RSS



























REAL NAMES ONLY: All posters must use their real individual or business name. This applies equally to Twitter account holders who use a nickname.
0 Comments
You can be the first one to leave a comment.